Key points
- Japan’s medical‑device sector offers consistent manufacturing quality backed by strict national oversight.
- Stable domestic supplier networks support predictable performance in clinical environments.
- PMDA and MHLW enforce ISO‑aligned requirements for risk management, QMS, and lifecycle documentation.
- Human‑factors engineering is common, resulting in lighter, better‑balanced instruments.
- Japan demonstrates global leadership in diagnostic devices, especially endoscopy and imaging.
- Strong postmarket vigilance reduces field uncertainty.
- The koplight™ is a prime example of these strengths, through transparent materials, reliable illumination, and consistent construction.
The Made in Japan advantage
Medical device distributors work at the intersection of manufacturing standards and clinical expectations. Hospitals want instruments that behave predictably. Surgeons expect tools with consistent weight, clarity, and handling. Japan’s device ecosystem supports these expectations through conservative and exacting engineering, strict regulation, and a domestic market that demands reliability. METI’s Vision for the Medical Device Industry 2024 outlines how Japan relies on precision manufacturing, stable materials, and strong quality systems to maintain global competitiveness.
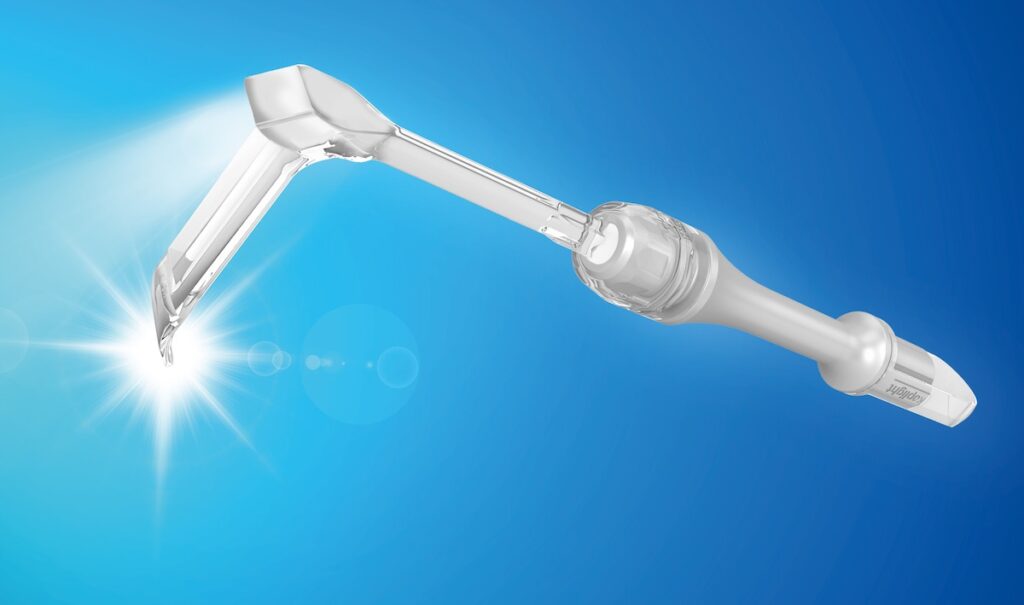
Light‑integrated devices such as the koplight™ show these traits in practice. Its transparent polycarbonate blade, steady LED output, and balanced handle reflect norms found across Japanese surgical instruments. Here are fact‑based advantages that “Made in Japan” devices provide to distributors.
Japan’s device ecosystem blends high-grade materials, conservative engineering, and detailed process controls. Retractors, including Japan‑made systems like the Yasui koplight™, which feature transparent, nonconductive blades and stable LED systems, and craftsmanship, strongly show these tendencies.
Here are evidence-based advantages that distributors (and their clients) gain from “Made in Japan” medical devices.
Contents
Proven manufacturing stability
Japan’s industrial structure prioritizes repeatability. METI notes that Japan’s manufacturing strengths include long‑term supplier partnerships, low‑variance processes, and careful engineering refinement. These conditions reduce shifts in product performance across production runs.
For distributors, this lowers the rate of unit‑to‑unit variation and decreases the chance of returns. Lighted retractors like the koplight™ benefit from stable molding and optical‑component assembly, so illumination and blade clarity remain consistent.
Regulatory rigor and traceability systems
Japan regulates medical devices under the Pharmaceutical and Medical Devices Act. PMDA review ties product safety and efficacy to ISO 14971 risk‑management standards and requires detailed documentation through the product lifecycle. MHLW ordinances align Japan’s QMS requirements with ISO 13485. PMDA also enforces structured postmarket reporting obligations, as outlined in Post‑Marketing Safety Measures and Risk Management.
Hospitals rely on this structure during audits and procurement. Many request device histories, lot tracking, and corrective‑action documentation. Japanese manufacturers typically supply these records in standardized formats, which reduces confusion and shortens review cycles.
Material quality and durability
Japan’s device sector relies heavily on high‑quality domestic materials and precision components. A government‑hosted industry overview notes that Japan’s medical device makers draw on national strengths in microfabrication, electronics, and materials technologies to support high‑accuracy diagnosis and less‑invasive therapy (Medical Equipment & Devices in Japan). Advanced polymers and alloys appear in many instruments because they offer predictable strength and stability.

A review of plastics in medical devices notes that medical‑grade polycarbonate delivers clarity, strength, and compatibility with sterilization (PMC7151894). The koplight™ uses transparent polycarbonate blades, allowing surgeons to see through the retractor while reducing glare. Consistent material quality lowers the chance of surface defects and supports durable performance.
Engineering focused on operator comfort
Human‑factors engineering shapes many Japanese surgical instruments. Studies in Applied Ergonomics and surgical‑handle analyses show that weight balance, handle geometry, and grip angle affect wrist posture, fatigue, and overall performance.
The koplight™ incorporates these principles. Its low weight, balanced center of gravity, and LED placement reduce surgeon strain and improve visibility. This often results in smoother demos and fewer follow‑up support cases for distributors.
Demonstrated leadership in diagnostic devices
Japan holds measurable global advantages in several diagnostic device categories. A Japan SPOTLIGHT review reports that Japanese firms command approximately 35% of the global market in major diagnostic fields and supply 99.1% of the world’s endoscopes. Japanese companies also hold strong positions in CT, MRI, and ultrasound manufacturing.
This leadership shapes procurement behavior. Hospitals often associate Japanese diagnostic devices with reliability, tight tolerances, and stable performance. Several device classes illustrate this, including rigid and flexible endoscopes, where Japanese firms dominate global market share; high-resolution ultrasound systems known for low noise and stable beam-forming; and CT and MRI platforms noted for rapid gantry cycles and dependable electronics. These strengths make Japanese diagnostic equipment a trusted reference point during procurement, even for unrelated device categories.
Postmarket vigilance and predictable field performance
Japan enforces fast, structured reporting of malfunctions and adverse events (PMDA safety measures). PMDA requires reporting within 15 to 30 days depending on event severity, as outlined in its safety measures guidance. A review in WHO Drug Information notes that strong postmarket systems help detect problems early and reduce downstream risk.
For distributors, these rules mean clearer communication when issues arise and faster resolution of component‑level concerns. Japan’s system also requires manufacturers to submit Field Safety Corrective Action (FSCA) reports and maintain documented timelines for follow‑up investigations, which helps hospitals track corrective progress.
PMDA’s public safety database makes many of these notices accessible, creating pressure for timely responses and transparent root‑cause analysis. LED‑based devices such as the koplight™ benefit from this structure because manufacturers must document investigations, submit updates, and close cases under defined regulatory expectations.
Business impacts for distributors
These characteristics affect daily distribution work in direct, measurable ways, shaping how distributors manage inventory, support clinical teams, address compliance checks, and plan for long‑term product performance.
Operational outcomes
- Lower return and complaint rates.
- Easier compliance documentation.
- Smoother demos and training sessions.
- Clear, standardized records for hospital committees.
Commercial outcomes
- Reduced warranty and service burden.
- Higher customer confidence.
- Stable long‑term product portfolios.
- A strong alternative to high‑volume, low‑cost production models.
Japan vs. another competitive region
This table summarizes key differences between Japanese systems and another high‑reliability region. Sources include METI’s industry vision and peer‑reviewed regulatory comparisons (MDPI regulatory review).
| Category | Japan | Europe |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory pathways | PMDA review, defined risk classes, strong QMS enforcement | European Medical Device Regulation (EU MDR) system with varied notified-body processes |
| Domestic quality pressure | High expectations in a large home market | Strong markets but uneven across member states |
| Reputation | Known for precision, reliability, and stable performance in diagnostic equipment such as endoscopy and imaging | Recognized for broad device portfolios across diagnostics and implants, supported by multinational manufacturers under EU MDR |
| Manufacturing norms | Emphasis on precision, stable suppliers, and long-term process control | Wide range of manufacturing scales and approaches across EU member states |
| Documentation style | Standardized templates and strict change control | Differs by notified body and country |
| Postmarket culture | Fast reporting timelines and structured corrective actions | Strong but less uniform enforcement |
Conclusion
Japanese medical devices offer distributors stable manufacturing, strict regulation, reliable materials, and surgeon‑centered engineering. Japan’s diagnostic‑device leadership reinforces trust among clinicians and procurement teams. The koplight™ illustrates how these elements converge in a single tool through clear materials, balanced handling, and steady illumination. These qualities reflect why “Made in Japan” continues to signal reliability in clinical practice.

Add the Japan-made koplight™ to your lineup
The koplight™ gives distributors a dependable, easy-to-position illuminated retractor backed by Japan’s manufacturing and regulatory strengths. Its transparent blade, stable lighting, and ergonomic balance support predictable use in operating rooms, which makes it a practical addition to your surgical portfolio.
If you want to explore distribution opportunities or discuss market fit in your region, contact us for details. Our team can provide specifications, training guidance, and support for evaluation in clinical settings.

