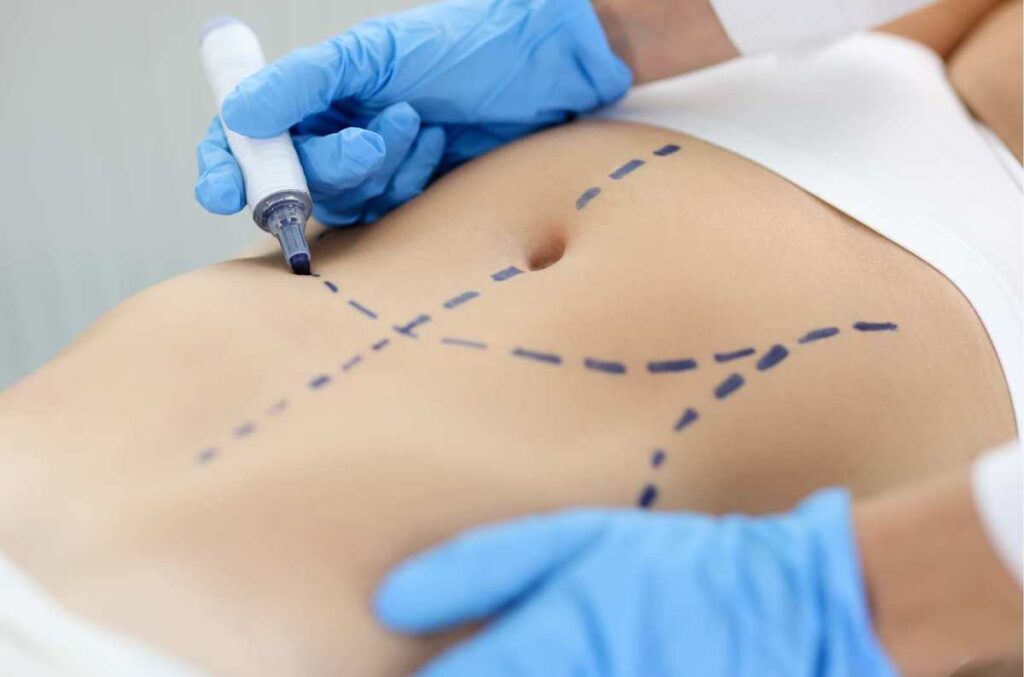
Drawing on or marking patients as part of pre-operative preparation plays a key role in surgical procedures. The markings serve as vital guides for the surgical team. They help establish clear communication between patients and the operating team, effectively reducing confusion and potential pre-operative mistakes. The markings also assist surgeons with the technicalities of their procedures.
This article explores the main reasons behind this practice and its importance in surgery.
1. Identifying a surgical site
Preoperative surgical site identification by marking is an essential and mandated step in preoperative patient preparation. International organizational guidelines, including the WHO Safer Surgery Checklist and High 5s: Standard Operating Procedures, emphasize the significance of this practice. Viewing it as an active preventive measure by the entire surgical team, which ensures and promotes patient safety and eliminates the occurrence of wrong-site surgery (WSS) – considered a “never event” (one that should not occur if safety procedures are followed properly).
Identifying and marking the surgical sites for all procedures involving incisions, percutaneous punctures, or instrument insertion is crucial. As a result, surgeons or assigned surgical team members are responsible for clearly marking the intended incision site or as close as possible to it.
This simple measure significantly helps prevent wrong-site errors, which statistics estimate occur at an alarming rate of 40 times per week in hospitals and clinics in the United States alone. Such a high number for a never event underscores the importance in ensuring patient safety.
Surgical site marking is common in various medical specialties, notably in orthopedic and gynecologic surgeries. For instance, in arthroscopy preoperative preparation, surgeons frequently mark the specific knee, hip, or shoulder that requires the procedure (laterality right vs. left) and indicate the incision’s precise location (level).
2. Planning an incision
Planning a skin incision is one of the most underrated parts of a surgical procedure. Yet, this aspect is vital for adhering to a fundamental rule in surgery: creating an incision that ensures both comfort for the surgeon and provides sufficient access to the pathology area.
Identifying and pre-operatively marking the “ideal” incision site involves careful consideration of anatomical landmarks, pathology, and imaging data. Surgeons go a step further by marking the length and orientation of their intended incision.
These meticulous efforts result in an intraoperative advantage, as they enable the surgical team to create an incision that provides direct access to the target area and is of sufficient size to facilitate the necessary surgical maneuvers. All while minimizing any potential damage to surrounding tissues.
3. Communication among the surgical team
At its core, surgical site marking strives to foster a culture of effective communication, teamwork, and common understanding among the surgical team members (HUDDLE UP).
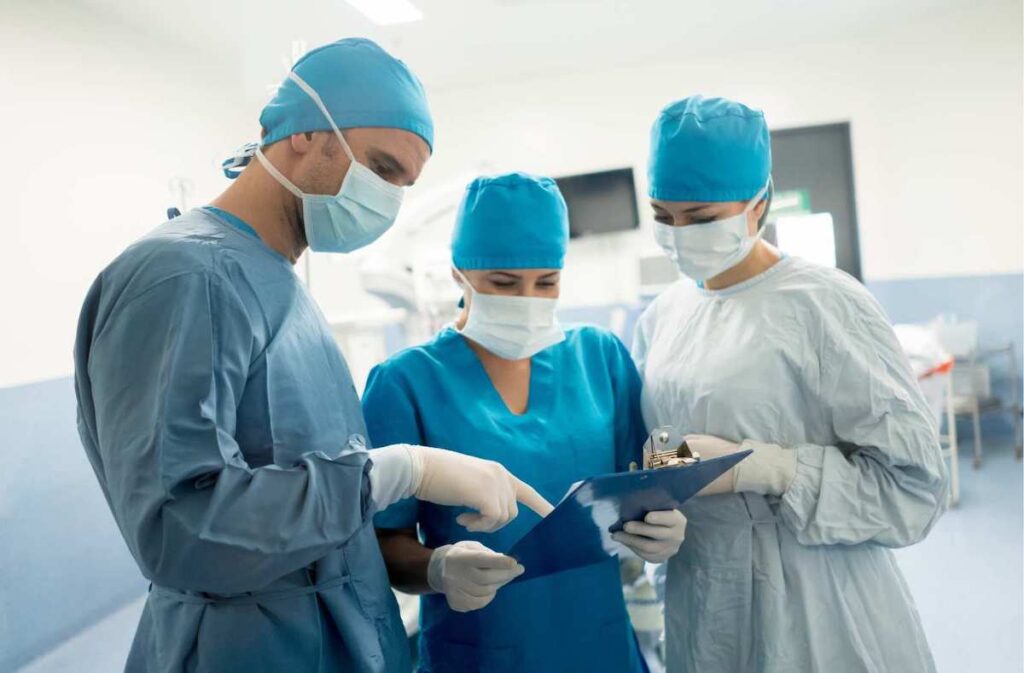

The simple communication created through surgical site marking accomplishes several important goals in surgical care. These include:
- Promoting active discussions and exchanges between team members during the marking process. This encourages open dialogue and the sharing of valuable insights.
- Identifying and confirming the planned approach.
- Assuring that everyone is on the same page, thus minimizing misunderstandings and potential errors during the procedure.
- The ability to collectively (surgeons, anesthesiologists, nurses, etc.) review and verify markings before the operation, promoting a collaborative, comprehensive, and safe approach to patient care.
4. Orientation
Surgical marking plays is vital in assisting surgeons with orientation during the procedure.
These markings serve as immediate visual reference points that aid in the surgeon’s orientation and understanding of the patient’s anatomy.
This orientation level is especially crucial in complex surgeries involving intricate structures such as vasculature and nerves. During such cases, detailed markings can help enhance the surgeon’s spatial awareness and facilitate precise surgical maneuvers, minimizing the risk of injury to these structures.
Orientation markers can also be useful in minimally invasive or endoscopic surgeries. As these approaches present challenges related to limited visibility and reduced tactile feedback, surgical site markings can help serve as a fixed reference point on the patient’s body. For example, surgeons can use marked incision points during endoscopic surgeries to quickly reorient themselves and reposition their instruments without a direct view of the patient’s anatomy.
5. Gaining patient consent
Surgical site marking is one of the crucial components of the informed consent process. It acts as one of the chief methods through which the most important team member, the patient, can actively participate in the surgical process.

According to the WHO standard operating procedures (High 5s), surgical site marking should be done with reference to the “source of truth”. This means surgeons should perform pre-operative marking in collaboration with awake, alert patients, and in reference to signed consent forms already marked with the correct sites. This process serves two purposes:
- By visibly marking the surgical site, the patient can physically see and confirm the location of the intended incision. This visual representation empowers the patient to understand the surgical plan better and ensures that the surgeon is operating on the correct body part.
- This active involvement enhances the patient’s autonomy and promotes a shared decision-making process, ensuring that the patient’s preferences and concerns are considered.
6. Identifying landmarks
Surgical site marking is a valuable aid in identifying landmarks during surgical procedures. These landmarks encompass specific anatomical structures or reference points, including bones, joints, vessels, and nerves, which are crucial guides for the surgeon to navigate the patient’s anatomy.
By visually highlighting these landmarks on the skin’s surface, the surgical team gains constant indicators and clear reference points throughout the procedure. This visual guidance facilitates safe navigation through the patient’s anatomy, ensuring that vital anatomical elements remain undamaged during the surgery. For instance, studies have shown that preoperative marking of the superficial peroneal nerve and its branches before anterior ankle arthroscopy can significantly reduce the incidence of nerve injury.
Moreover, landmark identification through surgical marking is equally vital for pre-operative anesthetic preparation. By accurately identifying and marking surface landmarks like vertebral processes, the surgical team can ensure precise administration of thoracic and lumbar paravertebral blocks, enhancing the efficacy and safety of anesthesia.
7. Cosmetic procedures
Surgical marking of body tissues holds particular significance for cosmetic procedures. Pre-operative marking in surgical and aesthetic procedures promotes optimal outcomes, patient safety, and overall satisfaction.
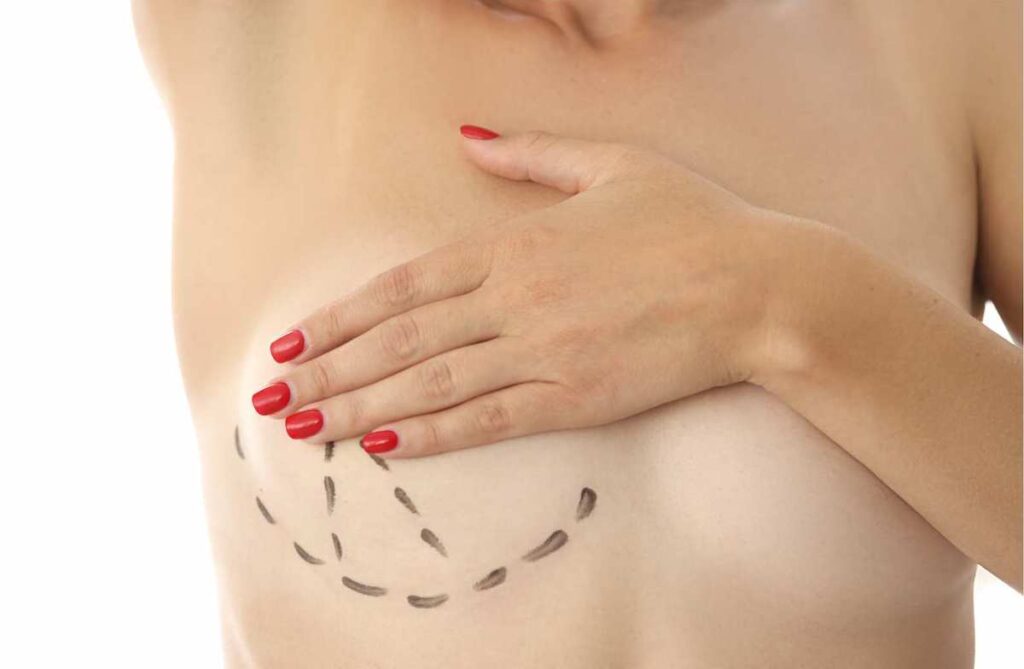
Whether it’s facelifts, breast augmentations, liposuction, or other cosmetic surgeries, marking the surgical site is a critical preparatory step. The benefits and the roles of body tissue marking in cosmetic procedures include:
- Precision and symmetry: Cosmetic surgeries often aim to enhance or alter specific features to achieve a more aesthetically pleasing result. Surgical site marking allows the surgeon to precisely plan and execute incisions or tissue removal, ensuring symmetry and balanced results. Marking the exact location of incisions, injection sites, or areas for liposuction guides the surgeon to achieve the desired cosmetic goals with greater accuracy.
- Communication and patient satisfaction: Marking the surgical site involves clear communication between the surgeon and the patient. This process allows the patient to visualize and understand the intended changes or improvements, ensuring their expectations align with the surgeon’s approach. Patient involvement and understanding contribute to increased satisfaction and reduce the likelihood of post-surgery regrets.
- Mitigating risk: In cosmetic surgeries, safety is paramount. By carefully marking the surgical site, the surgeon can avoid vital structures, nerves, and blood vessels, minimizing the risk of complications or unintended damage during the procedure.
- Minimizing scarring: In many cosmetic procedures, surgeons aim to keep incisions as discreet as possible. Precise site marking allows the surgeon to strategically place incisions in natural creases or hidden areas, minimizing scarring and more inconspicuous results.
- Reducing revisions: Proper site marking helps ensure that the surgeon achieves the desired outcome in the initial surgery. This can reduce the need for revision procedures, saving the patient from additional expenses, recovery time, and potential complications.